
The notations sin −1( x), cos −1( x), tan −1( x), etc., as introduced by John Herschel in 1813, are often used as well in English-language sources, much more than the also established sin ( x), cos ( x), tan ( x),-conventions consistent with the notation of an inverse function, that is useful e.g. In computer programming languages, the inverse trigonometric functions are often called by the abbreviated forms asin, acos, atan. If you run this code it will provide a good visual illustration of the pattern of data that is produced. graph algebra equations on a ti 84 free online maths quiz for yr 9s. Thus in the unit circle, "the arc whose cosine is x" is the same as "the angle whose cosine is x", because the length of the arc of the circle in radii is the same as the measurement of the angle in radians. This example produces a graph of 0 to 100. Inmediatamente obtendrs el valor del arcoseno expresado en grados o en radianes. When measuring in radians, an angle of θ radians will correspond to an arc whose length is rθ, where r is the radius of the circle.
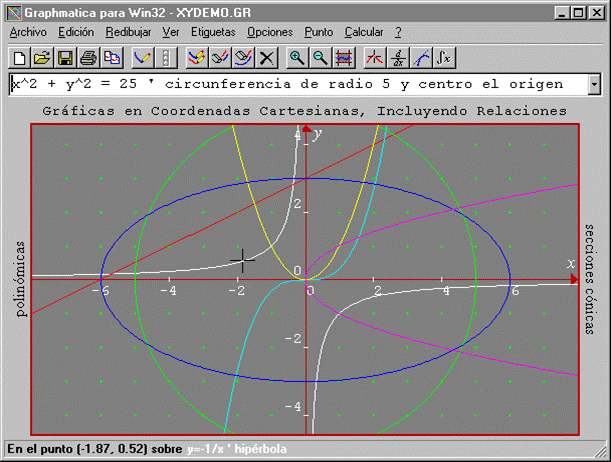
Tiene todas las caractersticas de la versin para Windows 3.1, ms todas las sutilezas hechas posibles por la plataforma Win32: Barra de herramientas standard con imgenes en colores y ayuda sobre. Graphmatica para Win32 fue diseado especialmente para Windows 95 y Windows NT 3.51 o posteriores. (This convention is used throughout this article.) This notation arises from the following geometric relationships: GRAPHMATICA: Grafica todo tipo de Funciones. The most common convention is to name inverse trigonometric functions using an arc- prefix: arcsin( x), arccos( x), arctan( x), etc. For basic things creating a new function.
ARCOSENO EN GRAPHMATICA HOW TO
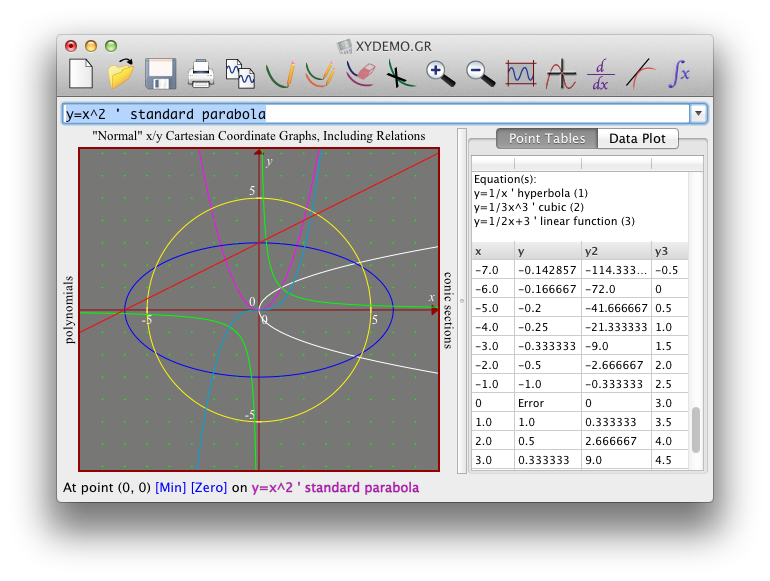
Several notations for the inverse trigonometric functions exist. In the following sections we begin to do things with function, such as learning how to graph functions with Julia.

See also: Trigonometric functions § Notation


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
